
Junel FE 1/20 Birth Control
Application & Dosage
👉 Looking to buy birth control? Order Junel FE Birth Control online, or browse all Birth Control options.
Introduction
The generic version of this birth control is Ethinyl estradiol 0.02 mg and norethindrone acetate 1 mg [24 tablets] and ferrous fumarate 75 mg [4 tablets] . Similar brand names to this medication are: Junel FE 1/20, Microgestin® Fe 1/20, Aurovela FE 1/20, Blisovi 24 Fe, Blisovi FE 1/20, Gildess FE 1/20, Hailey FE 1/20, Larin Fe 1/20, Loestrin Fe 1/20, Tarina FE 1/20,
This birth control plan reviews the risks and benefits of the treatment we are recommending. Please make sure to read it and the manufacturer's pamphlet that comes with the medicine. The manufacturer's pamphlet contains the full information on interactions, side effects, and other important information you should know about the medicine before you start.
Instructions
You have stated that you wish to take oral contraception pills to prevent pregnancy, ease painful periods, and in some instances to treat acne. This combination hormone medication is used to prevent pregnancy. It contains 2 hormones: norethindrone (a progestin) and ethinyl estradiol (an estrogen). It works mainly by preventing the release of an egg (ovulation) during your menstrual cycle. It also contains Iron (Fe) supplement to help replenish iron in your body that is lost during menstruation. Dose should be taken at the same time each day, preferably either after the evening meal or at bedtime.
When to Start
Schedule 1 (Sunday starter): Dose begins on first Sunday after onset of menstruation; if the menstrual period starts on Sunday, take the first tablet that very same day. With a Sunday start, an additional method of contraception should be used until after the first 7 days of consecutive administration.
Schedule 2 (Day 1 starter): Dose starts on the first day of menstrual cycle taking 1 tablet daily.
Switching from a different contraceptive:
- Oral contraceptive: Start on the same day that a new pack of the previous oral contraceptive would have been taken
- Transdermal patch, vaginal ring, injection: Start on the day the next dose would have been due
- IUD or implant: Start on the day of removal According to the manufacturer, if severe diarrhea or vomiting occur within 3 to 4 hours after taking an active tablet, back-up contraceptive measures may be needed.
Refills
You will automatically be sent a refill every 90 days (subject to a refill visit to help screen for side effects). You may request a refill early by logging into your Account (Subscriptions > Next Refill) or placing a new one-time order. If you decide to stop treatment prior to using your complete subscription please contact us for further guidance.
Active Ingredients
- Ethinyl estradiol (Estrogen analog)
- Norethindrone acetatel (progesterone analog)
- Ferrous Fumarate (Iron Supplement)
Allergies/Contraindications
True anaphylactic allergic reactions to oral contraception are extremely rare because the active ingredients in these medications mimic naturally occurring hormones in your body. However these medications do have other ingredients that may cause allergic reactions. If you experience any of the symptoms below, you should immediately go to the emergency room or call 911. This list is not all inclusive
- Allergic reaction like: rash, hives, itching, red, swollen, blistered, or peeling skin with or without fever, wheezing, tightness in the chest or throat, trouble breathing, swallowing, or talking, unusual hoarseness, or swelling of the mouth, face, lips, tongue, or throat.
- Liver problems like: dark urine, feeling tired, not hungry, upset stomach or stomach pain, light-colored stools, throwing up, or yellow skin or eyes.
- Signs of a blood clot like: chest pain or pressure, coughing up blood, shortness of breath, swelling, warmth, numbness, change of color, or pain in a leg or arm, trouble speaking, or swallowing
There are several contraindications to taking hormonal combined contraception. If you have any of the following conditions please let your doctor know prior to starting medication:
- Adrenal insufficiency
- Current or history of estrogen or progesterone sensitive cancer
- Hepatic tumors
- Pregnancy
- Renal impairment
- Undiagnosed abnormal uterine bleeding
- Taking hepatitis c drugs (ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir with or without dasabuvir)
- Prolonged immobilization
- Lupus with unknown of positive antiphospholipid antibody status
- Diabetes with a history of vascular disease or diabetes history >20 years
- Current gallbladder disease without surgical intervention
- Postpartum less than 6 weeks
- Recipient of organ transplant
- Porphyria
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Bariatric surgeries (Roux-en-y & biliopancreatic diversion)
- Advised by a healthcare provider to not take hormones
- Menopause
- Pancreatitis initiated on contraceptives in the past
Use is also contraindicated in women at high risk of having a blood clot or arterial or venous thrombotic diseases including:
- Cerebrovascular disease or history of strokes
- Coronary artery disease or history of heart attack
- Diabetes with a history of vascular disease or diabetes history >20 years
- Current or history of DVT (deep vein thrombosis) or PE (pulmonary Embolism)
- Hyper Coagulopathies (easy to make blood clots) (inherited or acquired),
- Hypertension or high blood pressure (uncontrolled)
- Headaches with focal neurological symptoms or migraines headaches with aura (with or without aura in >35 years old)
- Thrombogenic valvular or rhythm diseases of the heart (eg, subacute bacterial endocarditis with valvular disease or atrial fibrillation)
- 35+ years old who smoke
Conditions
We have evaluated your health history and the specific health information you provided us, however if anything changes and you develop or discover that one of these conditions applies to you please stop taking this medicine and call or message us immediately.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Use is contraindicated in pregnant women. Combination hormonal contraceptives are used to prevent pregnancy; treatment should be discontinued if pregnancy occurs. In general, the use of combination hormonal contraceptives, when inadvertently used early in pregnancy, have not been associated adverse fetal or maternal effects
Due to the increased risk of blood clots in legs postpartum, combination hormonal contraceptives should not be started in breastfeeding women <21 days following delivery. The risk of getting a blood clot decreases to population baseline by postpartum day 42. Use of combination hormonal contraceptives in women between 21 and 42 days after delivery should take into consideration the individual woman's risk factors for Getting a blood clot (eg, age ≥35 years, previous blood clot, thrombophilia, immobility, preeclampsia, transfusion at delivery, cesarean delivery, peripartum cardiomyopathy, BMI ≥30 kg/m2, postpartum hemorrhage, or smoking). The risks, benefits, and alternatives to combination hormonal contraception should be evaluated when initiating treatment in breastfeeding women. This should be discussed with your doctor who delivered your child prior to starting treatment.
Combination based birth controls with estrogen may impact your milk supply. If you would like an alternative contraceptive that won't impact your milk supply we recommend a progestin only pill.
Emergency Side Effects
This medicine can cause dangerous and potentially life threatening side effects. If any of the emergency side effects listed in the manufacturer's pamphlet happen to you please stop taking the medicine and call 911 or seek immediate medical help in person. This list can include (but are not limited to):
- Anaphylaxis/anaphylactoid reaction (shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, facial swelling or edema, tongue swelling)
- Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes)
- Chest pain
- Visual changes
- Sudden severe headache
- One sided or persistent leg pain
- Weakness or numbness in your extremities
- Trouble speaking
Other Side Effects
- Edema (swelling in legs)
- Worsening of varicose veins
- Depression
- Melasma (brownish skin, on the forehead, nose, upper lip, and cheeks)
- Amenorrhea (loss of period)
- Breast Changes: breast enlargement, discharge, tenderness, pain
- Increased or decreased Weight
- Changes in menstrual flow
- Abdominal cramps, bloating, nausea, vomiting
- Breakthrough bleeding, spotting, changes in secretions
- Yeast infection
- Change in sexual drive
- Acne
- Headaches
- Bloating
- Vaginal discharge
Medicines, Supplements, and Foods
We have evaluated your health history and the specific health information you provided us, however if anything changes and you start or discover that you are taking any of the medicines, foods, or supplements listed below call or message us before you take the medicine. Some of these can cause your birth control to be less effective and cause more severe or dangerous side effects. Alternative method of contraceptive (male condoms) Should be used if you are taking these medications:
- Antibiotics: Rifampin
- Anticonvulsants or anti-seizure medications such as carbamazepine (Tegretol®), phenytoin (Dilantin®), oxcarbazepine (Trileptal®), primidone, Lamotrigine (Lamictal®) or topiramate (Topamax®)
- Antifungal medications such as griseofulvin (Gris-PEG®), ketoconazole (Extina®, Nizoral®, Xolegel®)
- Antiretrovirals: ritonavir, ombitasvir, paritaprevir, dasabuvir
- Herbal medications such as St. John’s wort & DIM
- HIV Medications
- Modafinil (Provigil®)
- Barbiturates like Phenobarbital
- Ella (Ulipristal Acetate)
Accurate Information
We have evaluated the specific health information you provided and are making our recommendations based on it. If you forgot to provide or incorrectly provided that information we may misdiagnose or fail to diagnose conditions that you may have which could affect our recommendation for treatment. If you need to clarify or update any information about your health you can message or call us anytime.
Treatment Failure/Missed Doses
The effectiveness of hormonal oral contraception is very high when it is consistently taken and doses are not missed. The average treatment failure for oral contraception is 6 pregnancies per 100 women. The biggest cause of pregnancy is missed doses.
If one dose is late (<24 hours since dose should have been taken) or if one dose is missed (24 to <48 hours since dose should have been taken): Take dose as soon as possible. Continue remaining doses at the usual time (even if that means 2 doses on the same day). No back up method is needed.
If 2 or more consecutive doses are missed (≥48 hours since dose should have been taken): Take the most recently missed dose as soon as possible, discard any other missed doses. Continue remaining doses at the usual time (even if that means taking 2 doses on the same day); use back-up contraception until hormonal pills have been taken for 7 consecutive days. You may experience irregular bleeding due to your missed doses.
You can also use this opportunity to have a menstrual cycle and can wait to restart your active tablets again after taking 4-7 days off of your birth control. If you have not missed any previous pills within your pill pack no backup method is needed. If you’ve missed previous pills throughout your pill pack, you should use a backup method during your off days and for the first 7 days of restarting your active pills.
Consider use of emergency contraception in some situations (refer to guidelines for details). Also refer to prescribing information for product specific information.
Accepting or Declining Our Recommendation
We are recommending this treatment for you because the potential benefits of treatment outweigh the risks. You should evaluate this information as well as the manufacturer's pamphlet, and any input from your in-person healthcare team, or other relevant information to decide if this treatment plan is appropriate for you. You are free to decline our treatment recommendations.
Alternative Treatment
We have based our recommendation on your specific case and current medical guidelines, but there may be alternative treatments or strategies that may be helpful to you. Some may be more or less effective than what we provide. Some treatments may require an in-person exam or procedure which we can't provide. Message us or talk to your doctor in-person to discuss alternative treatments. Here are some other treatments or strategies that you might consider:
- Implanon implant contraceptives
- Intrauterine device (IUD)
- Intermittent injections
- Transdermal patches
- Nuvaring
- Male or female condoms
- Diaphragm
- Spermicide
- Alternative oral contraceptive pill
- Sterilization
- Sponge
- Cap
- Diaphragm
- Fertility Awareness Method
- Phexxi
Share with Your In-Person Healthcare Team
You can access your records anytime. We strongly recommend that you update your in-person doctor, pharmacist, and the rest of your healthcare team to let them know about any new medicines you are taking or other changes in your health.
You can also ask us questions anytime and we are happy to help you share any information about your health with your in-person healthcare team.
Trusted Treatments
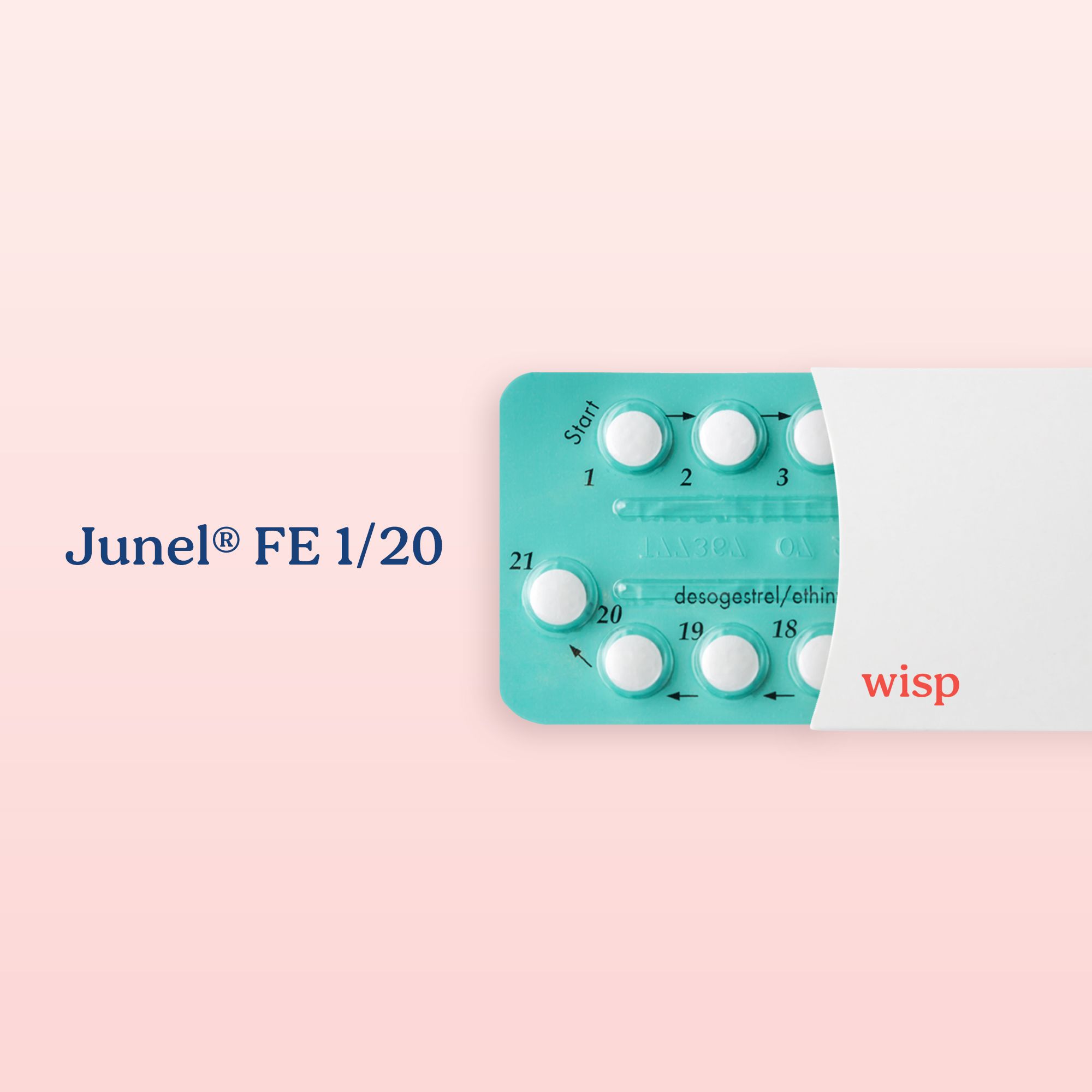
Junel FE 1/20® Birth Control (generic)
Similar to: Microgestin® Fe 1/20, Aurovela FE 1/20, Blisovi FE 1/20, Gildess FE 1/20, Hailey FE 1/20, Larin Fe 1/20, Loestrin Fe 1/20 and Tarina FE 1/20.
Starting at $15.00
Get Started
Skip Your Period
Skip Your Period long-term with birth control options delivered to your door.
Starting at $22.00
Get Started
Levonorgestrel (Generic PLAN B®)
Take Levonorgestrel as soon as possible but within 72 hours (3 days) of unprotected intercourse or contraceptive failure. Delivery only - order ahead of time!
Starting at $12.50
Get Started
Delay Your Period (Norethindrone Acetate Tablets)
Delay Your Period for up to 20 days for special events, competitions, or vacations. Not a form of birth control.
Starting at $39.00
Get Started